Python에서 대규모 평가 작업의 경우 evaluate()의 비동기 버전인 aevaluate() 사용을 권장합니다. 두 메서드는 동일한 인터페이스를 가지고 있으므로 비동기 평가 실행 가이드를 읽기 전에 이 가이드를 먼저 읽는 것이 좋습니다.JS/TS에서는 evaluate()가 이미 비동기이므로 별도의 메서드가 필요하지 않습니다.대규모 작업을 실행할 때는
max_concurrency/maxConcurrency 인자를 구성하는 것도 중요합니다. 이는 데이터셋을 스레드로 효과적으로 분할하여 평가를 병렬화합니다.애플리케이션 정의
먼저 평가할 애플리케이션이 필요합니다. 이 예제에서는 간단한 독성 분류기를 만들어 보겠습니다.Dataset 생성 또는 선택
애플리케이션을 평가할 Dataset이 필요합니다. 우리의 데이터셋에는 독성 및 비독성 텍스트의 레이블이 지정된 examples가 포함됩니다.langsmith>=0.3.13 필요
Evaluator 정의
일반적인 사전 구축된 evaluator를 위해 LangChain의 오픈 소스 평가 패키지 openevals도 확인할 수 있습니다.
- Python:
langsmith>=0.3.13필요 - TypeScript:
langsmith>=0.2.9필요
평가 실행
evaluate() / aevaluate() 메서드를 사용하여 평가를 실행합니다. 주요 인자는 다음과 같습니다:- 입력 dictionary를 받아 출력 dictionary를 반환하는 target function. 각 Example의
example.inputs필드가 target function에 전달됩니다. 이 경우 우리의toxicity_classifier는 이미 예제 입력을 받도록 설정되어 있으므로 직접 사용할 수 있습니다. data- 평가할 LangSmith 데이터셋의 이름 또는 UUID, 또는 예제의 iteratorevaluators- 함수의 출력을 채점할 evaluator 목록
langsmith>=0.3.13 필요
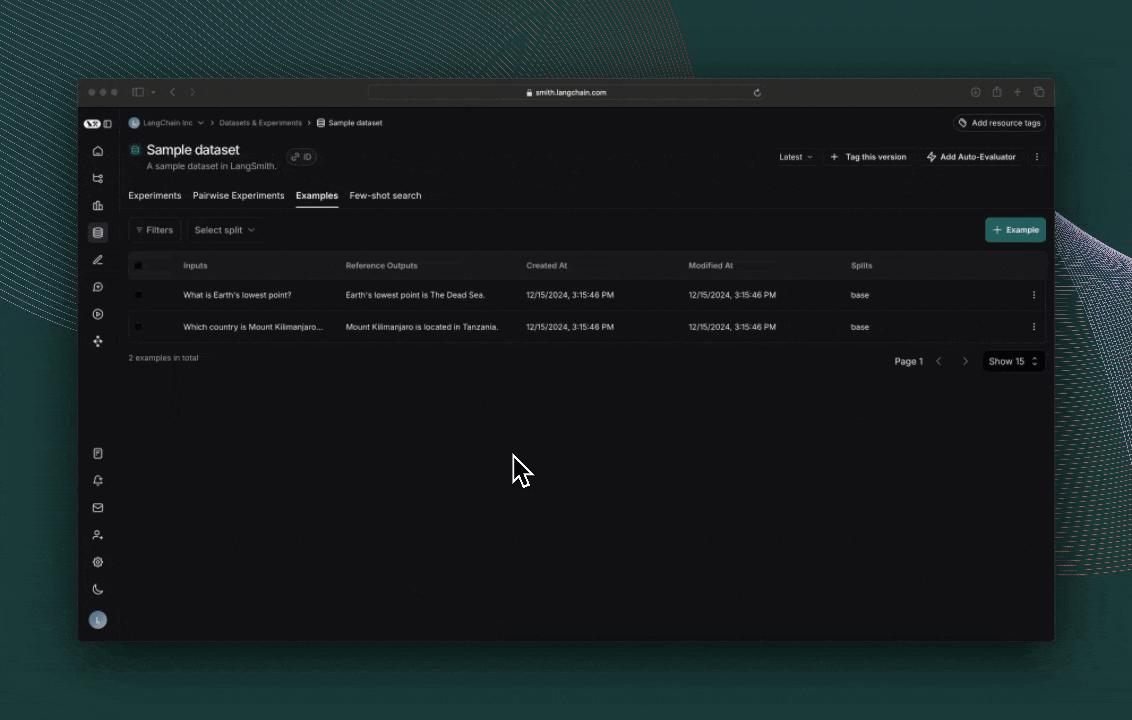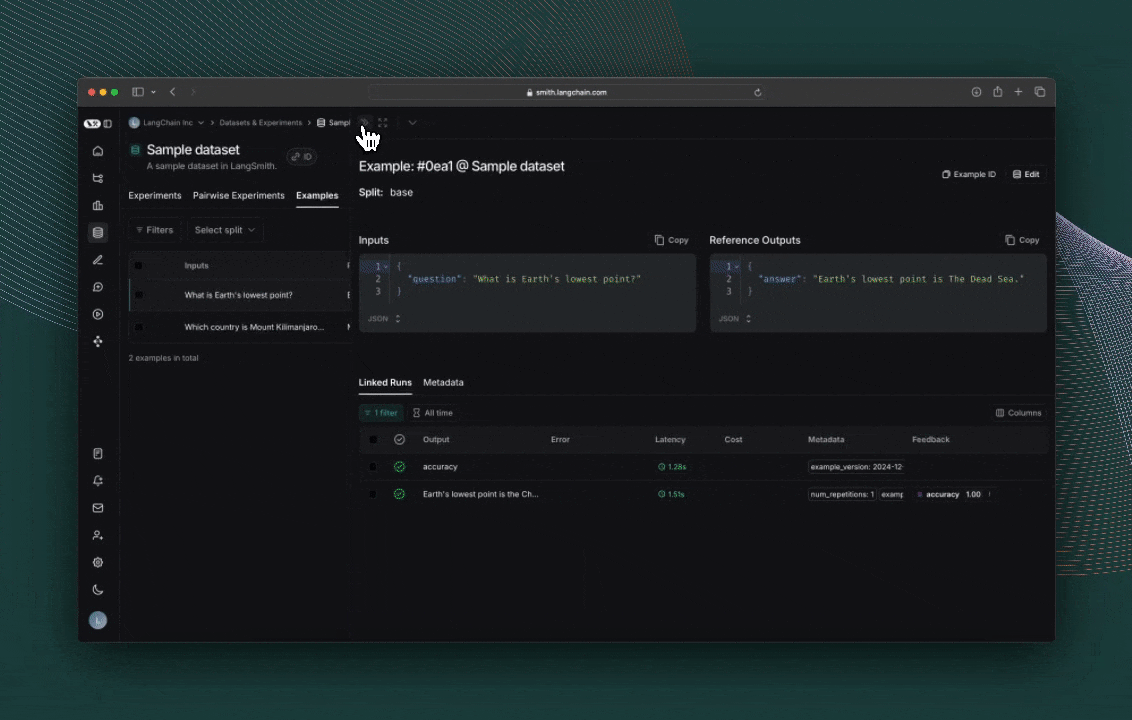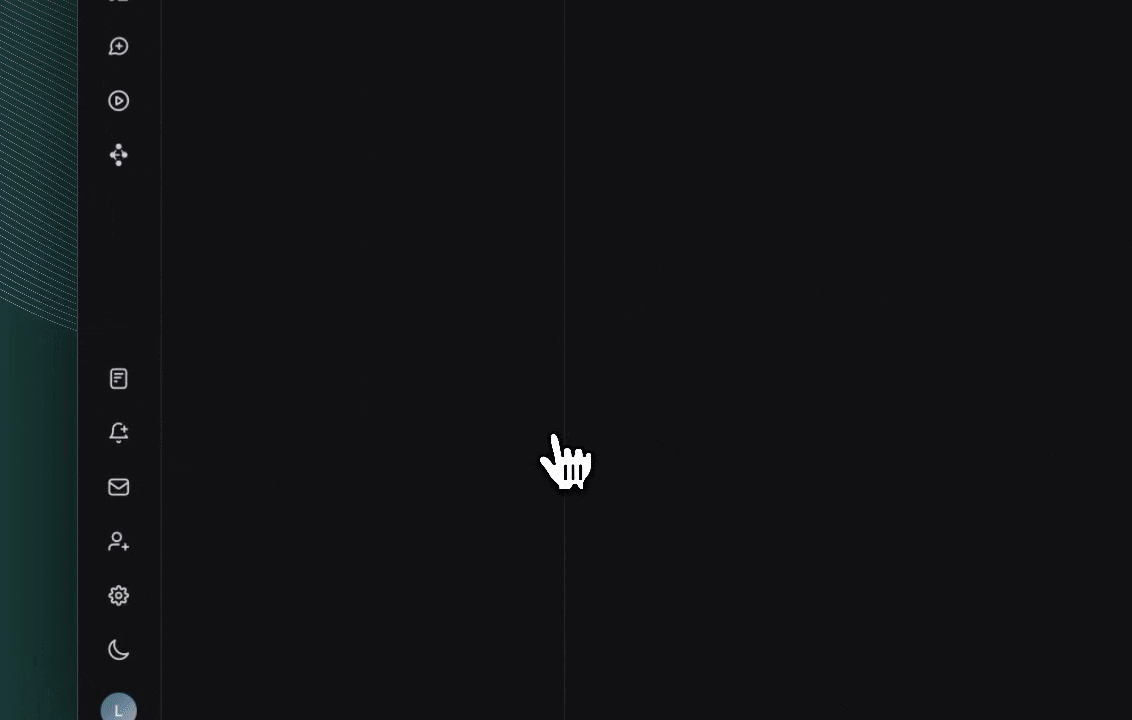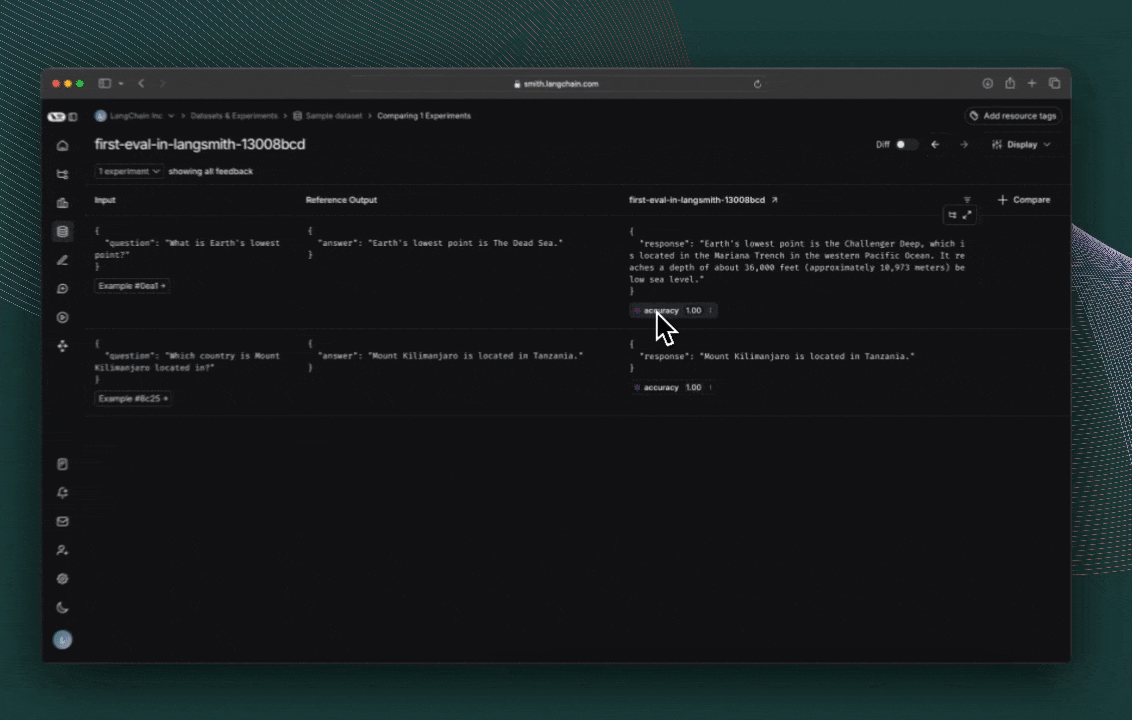
결과 탐색
evaluate()의 각 호출은 LangSmith UI에서 보거나 SDK를 통해 쿼리할 수 있는 Experiment를 생성합니다. 평가 점수는 각 실제 출력에 대해 feedback으로 저장됩니다.
tracing을 위해 코드에 주석을 추가한 경우, 사이드 패널 뷰에서 각 행의 trace를 열 수 있습니다.
참조 코드
통합된 코드 스니펫을 보려면 클릭하세요
통합된 코드 스니펫을 보려면 클릭하세요
관련 항목
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

