애플리케이션을 배포하는 것은 지속적인 개선 프로세스의 시작일 뿐입니다. 프로덕션에 배포한 후에는 프롬프트, 언어 모델, 도구 및 아키텍처를 개선하여 시스템을 정제하고 싶을 것입니다. 백테스팅은 과거 데이터를 사용하여 애플리케이션의 새 버전을 평가하고 새로운 출력을 원래 출력과 비교하는 것을 포함합니다. 프로덕션 전 데이터셋을 사용한 평가와 비교할 때, 백테스팅은 애플리케이션의 새 버전이 현재 배포된 버전보다 개선되었는지에 대한 더 명확한 지표를 제공합니다.
백테스팅의 기본 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
- 테스트할 프로덕션 추적 프로젝트에서 샘플 run을 선택합니다.
- run input을 dataset으로 변환하고 run output을 해당 dataset에 대한 초기 experiment로 기록합니다.
- 새로운 dataset에서 새 시스템을 실행하고 experiment 결과를 비교합니다.
이 프로세스는 대표적인 input의 새로운 dataset을 제공하며, 이를 버전 관리하고 모델 백테스팅에 사용할 수 있습니다.
종종 명확한 “ground truth” 답변을 사용할 수 없는 경우가 있습니다. 이러한 경우 출력에 수동으로 레이블을 지정하거나 참조 데이터에 의존하지 않는 evaluator를 사용할 수 있습니다. 애플리케이션이 ground-truth 레이블을 캡처할 수 있는 경우(예: 사용자가 피드백을 남길 수 있도록 허용), 이를 수행하는 것을 강력히 권장합니다.
Setup
환경 구성
환경 변수를 설치하고 설정합니다. 이 가이드는 langsmith>=0.2.4가 필요합니다.
편의를 위해 이 튜토리얼에서는 LangChain OSS 프레임워크를 사용하지만, 표시된 LangSmith 기능은 프레임워크에 구애받지 않습니다.
pip install -U langsmith langchain langchain-anthropic langchainhub emoji
import getpass
import os
# Set the project name to whichever project you'd like to be testing against
project_name = "Tweet Writing Task"
os.environ["LANGSMITH_PROJECT"] = project_name
os.environ["LANGSMITH_TRACING"] = "true"
if not os.environ.get("LANGSMITH_API_KEY"):
os.environ["LANGSMITH_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("YOUR API KEY")
# Optional. You can swap OpenAI for any other tool-calling chat model.
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "YOUR OPENAI API KEY"
# Optional. You can swap Tavily for the free DuckDuckGo search tool if preferred.
# Get Tavily API key: https://tavily.com
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = "YOUR TAVILY API KEY"
애플리케이션 정의
이 예제에서는 일부 인터넷 검색 도구에 액세스할 수 있는 간단한 트윗 작성 애플리케이션을 만들어 보겠습니다:
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun, TavilySearchResults
from langchain_core.rate_limiters import InMemoryRateLimiter
# We will use GPT-3.5 Turbo as the baseline and compare against GPT-4o
gpt_3_5_turbo = init_chat_model(
"gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature=1,
configurable_fields=("model", "model_provider"),
)
# The instrucitons are passed as a system message to the agent
instructions = """You are a tweet writing assistant. Given a topic, do some research and write a relevant and engaging tweet about it.
- Use at least 3 emojis in each tweet
- The tweet should be no longer than 280 characters
- Always use the search tool to gather recent information on the tweet topic
- Write the tweet only based on the search content. Do not rely on your internal knowledge
- When relevant, link to your sources
- Make your tweet as engaging as possible"""
# Define the tools our agent can use
# If you have a higher tiered Tavily API plan you can increase this
rate_limiter = InMemoryRateLimiter(requests_per_second=0.08)
# Use DuckDuckGo if you don't have a Tavily API key:
# tools = [DuckDuckGoSearchRun(rate_limiter=rate_limiter)]
tools = [TavilySearchResults(max_results=5, rate_limiter=rate_limiter)]
agent = create_agent(gpt_3_5_turbo, tools=tools, system_prompt=instructions)
프로덕션 데이터 시뮬레이션
이제 일부 프로덕션 데이터를 시뮬레이션해 보겠습니다:
fake_production_inputs = [
"Alan turing's early childhood",
"Economic impacts of the European Union",
"Underrated philosophers",
"History of the Roxie theater in San Francisco",
"ELI5: gravitational waves",
"The arguments for and against a parliamentary system",
"Pivotal moments in music history",
"Big ideas in programming languages",
"Big questions in biology",
"The relationship between math and reality",
"What makes someone funny",
]
agent.batch(
[{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": content}]} for content in fake_production_inputs],
)
프로덕션 Trace를 Experiment로 변환
첫 번째 단계는 프로덕션 input을 기반으로 dataset을 생성하는 것입니다. 그런 다음 모든 trace를 복사하여 baseline experiment로 사용합니다.
백테스트할 run 선택
list_runs의 filter 인수를 사용하여 백테스트할 run을 선택할 수 있습니다. filter 인수는 LangSmith trace query syntax를 사용하여 run을 선택합니다.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone
from uuid import uuid4
from langsmith import Client
from langsmith.beta import convert_runs_to_test
# Fetch the runs we want to convert to a dataset/experiment
client = Client()
# How we are sampling runs to include in our dataset
end_time = datetime.now(tz=timezone.utc)
start_time = end_time - timedelta(days=1)
run_filter = f'and(gt(start_time, "{start_time.isoformat()}"), lt(end_time, "{end_time.isoformat()}"))'
prod_runs = list(
client.list_runs(
project_name=project_name,
is_root=True,
filter=run_filter,
)
)
run을 experiment로 변환
convert_runs_to_test는 일부 run을 가져와서 다음을 수행하는 함수입니다:
- input과 선택적으로 output이 Example로 dataset에 저장됩니다.
- input과 output이 experiment로 저장되며, 마치
evaluate 함수를 실행하고 해당 output을 받은 것처럼 처리됩니다.
# Name of the dataset we want to create
dataset_name = f'{project_name}-backtesting {start_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")}-{end_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")}'
# Name of the experiment we want to create from the historical runs
baseline_experiment_name = f"prod-baseline-gpt-3.5-turbo-{str(uuid4())[:4]}"
# This converts the runs to a dataset + experiment
convert_runs_to_test(
prod_runs,
# Name of the resulting dataset
dataset_name=dataset_name,
# Whether to include the run outputs as reference/ground truth
include_outputs=False,
# Whether to include the full traces in the resulting experiment
# (default is to just include the root run)
load_child_runs=True,
# Name of the experiment so we can apply evalautors to it after
test_project_name=baseline_experiment_name
)
새 시스템과 벤치마크
이제 프로덕션 run을 새 시스템과 벤치마킹하는 프로세스를 시작할 수 있습니다.
Evaluator 정의
먼저 두 시스템을 비교하는 데 사용할 evaluator를 정의하겠습니다. 참조 output이 없으므로 실제 output만 필요한 평가 메트릭을 고안해야 합니다.
import emoji
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.messages import convert_to_openai_messages
class Grade(BaseModel):
"""Grade whether a response is supported by some context."""
grounded: bool = Field(..., description="Is the majority of the response supported by the retrieved context?")
grounded_instructions = f"""You have given somebody some contextual information and asked them to write a statement grounded in that context.
Grade whether their response is fully supported by the context you have provided. \
If any meaningful part of their statement is not backed up directly by the context you provided, then their response is not grounded. \
Otherwise it is grounded."""
grounded_model = init_chat_model(model="gpt-4o").with_structured_output(Grade)
def lt_280_chars(outputs: dict) -> bool:
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
return len(messages[-1]['content']) <= 280
def gte_3_emojis(outputs: dict) -> bool:
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
return len(emoji.emoji_list(messages[-1]['content'])) >= 3
async def is_grounded(outputs: dict) -> bool:
context = ""
messages = convert_to_openai_messages(outputs["messages"])
for message in messages:
if message["role"] == "tool":
# Tool message outputs are the results returned from the Tavily/DuckDuckGo tool
context += "\n\n" + message["content"]
tweet = messages[-1]["content"]
user = f"""CONTEXT PROVIDED:
{context}
RESPONSE GIVEN:
{tweet}"""
grade = await grounded_model.ainvoke([
{"role": "system", "content": grounded_instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": user}
])
return grade.grounded
Baseline 평가
이제 baseline experiment에 대해 evaluator를 실행해 보겠습니다.
baseline_results = await client.aevaluate(
baseline_experiment_name,
evaluators=[lt_280_chars, gte_3_emojis, is_grounded],
)
# If you have pandas installed can easily explore results as df:
# baseline_results.to_pandas()
새 시스템 정의 및 평가
이제 새 시스템을 정의하고 평가해 보겠습니다. 이 예제에서 새 시스템은 이전 시스템과 동일하지만 GPT-3.5 대신 GPT-4o를 사용합니다. 모델을 구성 가능하게 만들었으므로 에이전트에 전달되는 기본 config만 업데이트하면 됩니다:
candidate_results = await client.aevaluate(
agent.with_config(model="gpt-4o"),
data=dataset_name,
evaluators=[lt_280_chars, gte_3_emojis, is_grounded],
experiment_prefix="candidate-gpt-4o",
)
# If you have pandas installed can easily explore results as df:
# candidate_results.to_pandas()
결과 비교
두 experiment를 모두 실행한 후 dataset에서 확인할 수 있습니다:
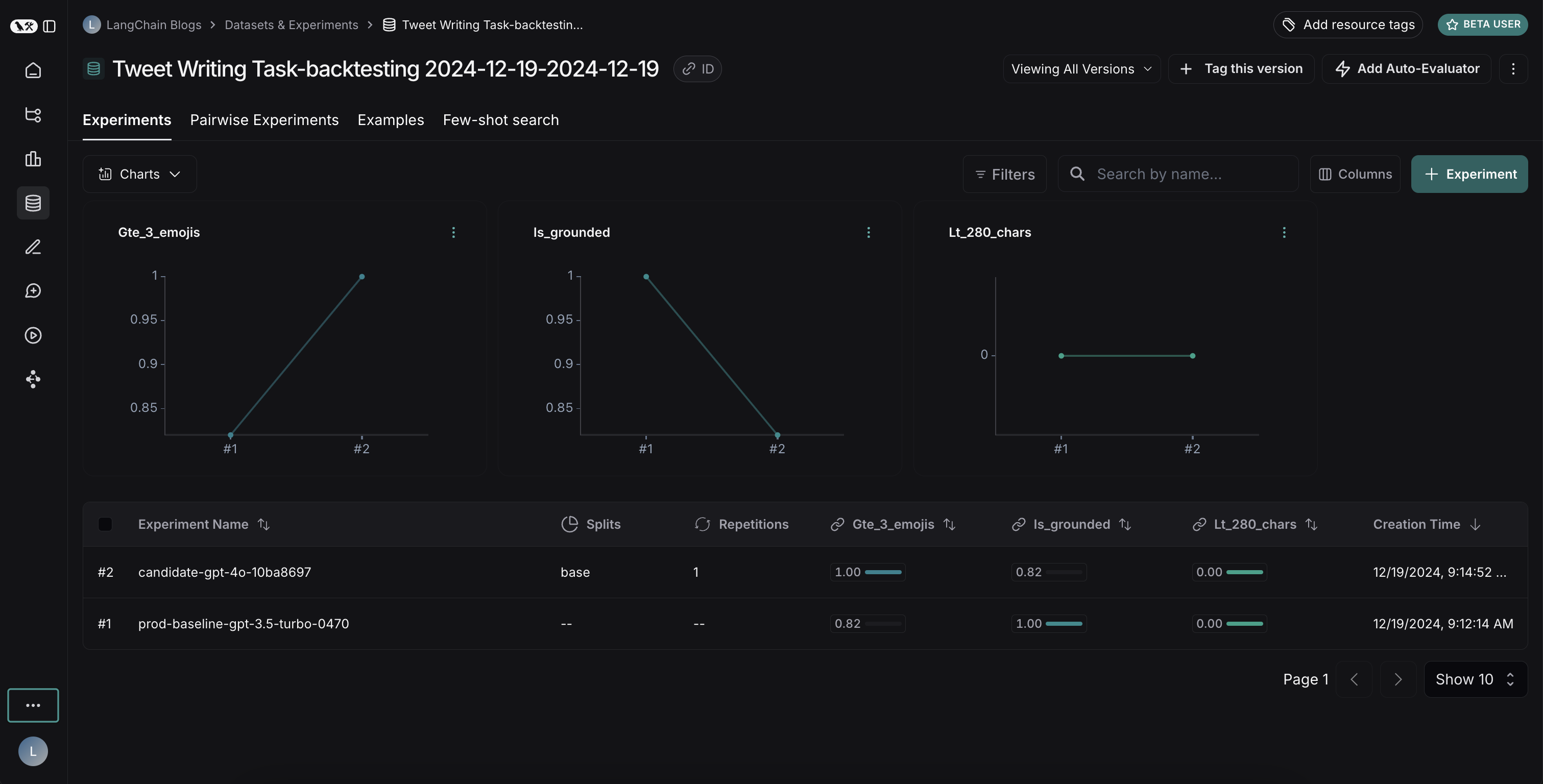 결과는 두 모델 간의 흥미로운 트레이드오프를 보여줍니다:
결과는 두 모델 간의 흥미로운 트레이드오프를 보여줍니다:
- GPT-4o는 형식 규칙을 따르는 성능이 향상되어 요청된 수의 이모지를 일관되게 포함합니다
- 그러나 GPT-4o는 제공된 검색 결과에 기반을 두는 데 있어 신뢰성이 떨어집니다
grounding 문제를 설명하자면: 이 예제 run에서 GPT-4o는 검색 결과에 없던 Abū Bakr Muhammad ibn Zakariyyā al-Rāzī의 의학적 기여에 대한 사실을 포함했습니다. 이는 제공된 정보를 엄격하게 사용하는 대신 내부 지식을 활용하고 있음을 보여줍니다.
이 백테스팅 실습은 GPT-4o가 일반적으로 더 유능한 모델로 간주되지만, 단순히 업그레이드하는 것만으로는 트윗 작성기를 개선할 수 없다는 것을 보여주었습니다. GPT-4o를 효과적으로 사용하려면 다음이 필요합니다:
- 제공된 정보만 사용하도록 더 강하게 강조하도록 프롬프트를 개선
- 또는 모델의 출력을 더 잘 제한하도록 시스템 아키텍처를 수정
이러한 통찰력은 백테스팅의 가치를 보여줍니다 - 배포 전에 잠재적인 문제를 식별하는 데 도움이 되었습니다.


 결과는 두 모델 간의 흥미로운 트레이드오프를 보여줍니다:
결과는 두 모델 간의 흥미로운 트레이드오프를 보여줍니다:


