- 단기 메모리 추가를 에이전트의 state의 일부로 추가하여 다중 턴 대화를 가능하게 합니다.
- 장기 메모리 추가를 통해 세션 간에 사용자별 또는 애플리케이션 수준 데이터를 저장합니다.
Add short-term memory
단기 메모리(thread-level persistence)는 에이전트가 다중 턴 대화를 추적할 수 있게 합니다. 단기 메모리를 추가하려면:Copy
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
builder = StateGraph(...)
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
graph.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi! i am Bob"}]},
{"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}},
)
Use in production
프로덕션 환경에서는 데이터베이스를 기반으로 하는 checkpointer를 사용하세요:Copy
from langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaver
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable"
with PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer:
builder = StateGraph(...)
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
예제: Postgres checkpointer 사용하기
예제: Postgres checkpointer 사용하기
Copy
pip install -U "psycopg[binary,pool]" langgraph langgraph-checkpoint-postgres
Postgres checkpointer를 처음 사용할 때는
checkpointer.setup()을 호출해야 합니다- Sync
- Async
Copy
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaver
model = init_chat_model(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-haiku-latest")
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable"
with PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer:
# checkpointer.setup()
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
response = model.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi! I'm bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what's my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
예제: [MongoDB](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-mongodb/) checkpointer 사용하기
예제: [MongoDB](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-mongodb/) checkpointer 사용하기
Copy
pip install -U pymongo langgraph langgraph-checkpoint-mongodb
설정
MongoDB checkpointer를 사용하려면 MongoDB 클러스터가 필요합니다. 클러스터가 없다면 이 가이드를 따라 생성하세요.
- Sync
- Async
Copy
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.mongodb import MongoDBSaver
model = init_chat_model(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-haiku-latest")
DB_URI = "localhost:27017"
with MongoDBSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer:
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
response = model.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi! I'm bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what's my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
예제: [Redis](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-redis/) checkpointer 사용하기
예제: [Redis](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-redis/) checkpointer 사용하기
Copy
pip install -U langgraph langgraph-checkpoint-redis
Redis checkpointer를 처음 사용할 때는
checkpointer.setup()을 호출해야 합니다- Sync
- Async
Copy
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.redis import RedisSaver
model = init_chat_model(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-haiku-latest")
DB_URI = "redis://localhost:6379"
with RedisSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer:
# checkpointer.setup()
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
response = model.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi! I'm bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what's my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Use in subgraphs
그래프에 subgraphs가 포함되어 있는 경우, 부모 그래프를 컴파일할 때만 checkpointer를 제공하면 됩니다. LangGraph는 자동으로 checkpointer를 자식 subgraph에 전파합니다.Copy
from langgraph.graph import START, StateGraph
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from typing import TypedDict
class State(TypedDict):
foo: str
# Subgraph
def subgraph_node_1(state: State):
return {"foo": state["foo"] + "bar"}
subgraph_builder = StateGraph(State)
subgraph_builder.add_node(subgraph_node_1)
subgraph_builder.add_edge(START, "subgraph_node_1")
subgraph = subgraph_builder.compile()
# Parent graph
builder = StateGraph(State)
builder.add_node("node_1", subgraph)
builder.add_edge(START, "node_1")
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
Copy
subgraph_builder = StateGraph(...)
subgraph = subgraph_builder.compile(checkpointer=True)
Add long-term memory
장기 메모리를 사용하여 대화 간에 사용자별 또는 애플리케이션별 데이터를 저장하세요.Copy
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
store = InMemoryStore()
builder = StateGraph(...)
graph = builder.compile(store=store)
Use in production
프로덕션 환경에서는 데이터베이스를 기반으로 하는 store를 사용하세요:Copy
from langgraph.store.postgres import PostgresStore
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable"
with PostgresStore.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as store:
builder = StateGraph(...)
graph = builder.compile(store=store)
예제: Postgres store 사용하기
예제: Postgres store 사용하기
Copy
pip install -U "psycopg[binary,pool]" langgraph langgraph-checkpoint-postgres
Postgres store를 처음 사용할 때는
store.setup()을 호출해야 합니다- Sync
- Async
Copy
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaver
from langgraph.store.postgres import PostgresStore
from langgraph.store.base import BaseStore
model = init_chat_model(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-haiku-latest")
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5442/postgres?sslmode=disable"
with (
PostgresStore.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as store,
PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer,
):
# store.setup()
# checkpointer.setup()
def call_model(
state: MessagesState,
config: RunnableConfig,
*,
store: BaseStore,
):
user_id = config["configurable"]["user_id"]
namespace = ("memories", user_id)
memories = store.search(namespace, query=str(state["messages"][-1].content))
info = "\n".join([d.value["data"] for d in memories])
system_msg = f"You are a helpful assistant talking to the user. User info: {info}"
# Store new memories if the user asks the model to remember
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if "remember" in last_message.content.lower():
memory = "User name is Bob"
store.put(namespace, str(uuid.uuid4()), {"data": memory})
response = model.invoke(
[{"role": "system", "content": system_msg}] + state["messages"]
)
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(
checkpointer=checkpointer,
store=store,
)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hi! Remember: my name is Bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "2",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
예제: [Redis](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-redis/) store 사용하기
예제: [Redis](https://pypi.org/project/langgraph-checkpoint-redis/) store 사용하기
Copy
pip install -U langgraph langgraph-checkpoint-redis
Redis store를 처음 사용할 때는
store.setup()을 호출해야 합니다- Sync
- Async
Copy
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.redis import RedisSaver
from langgraph.store.redis import RedisStore
from langgraph.store.base import BaseStore
model = init_chat_model(model="anthropic:claude-3-5-haiku-latest")
DB_URI = "redis://localhost:6379"
with (
RedisStore.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as store,
RedisSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer,
):
store.setup()
checkpointer.setup()
def call_model(
state: MessagesState,
config: RunnableConfig,
*,
store: BaseStore,
):
user_id = config["configurable"]["user_id"]
namespace = ("memories", user_id)
memories = store.search(namespace, query=str(state["messages"][-1].content))
info = "\n".join([d.value["data"] for d in memories])
system_msg = f"You are a helpful assistant talking to the user. User info: {info}"
# Store new memories if the user asks the model to remember
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if "remember" in last_message.content.lower():
memory = "User name is Bob"
store.put(namespace, str(uuid.uuid4()), {"data": memory})
response = model.invoke(
[{"role": "system", "content": system_msg}] + state["messages"]
)
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(
checkpointer=checkpointer,
store=store,
)
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hi! Remember: my name is Bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "2",
"user_id": "1",
}
}
for chunk in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Use semantic search
그래프의 메모리 store에서 semantic search를 활성화하여 그래프 에이전트가 의미적 유사성으로 store의 항목을 검색할 수 있도록 하세요.Copy
from langchain.embeddings import init_embeddings
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
# Create store with semantic search enabled
embeddings = init_embeddings("openai:text-embedding-3-small")
store = InMemoryStore(
index={
"embed": embeddings,
"dims": 1536,
}
)
store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "1", {"text": "I love pizza"})
store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "2", {"text": "I am a plumber"})
items = store.search(
("user_123", "memories"), query="I'm hungry", limit=1
)
semantic search를 사용한 장기 메모리
semantic search를 사용한 장기 메모리
Copy
from langchain.embeddings import init_embeddings
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.store.base import BaseStore
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
from langgraph.graph import START, MessagesState, StateGraph
model = init_chat_model("openai:gpt-4o-mini")
# Create store with semantic search enabled
embeddings = init_embeddings("openai:text-embedding-3-small")
store = InMemoryStore(
index={
"embed": embeddings,
"dims": 1536,
}
)
store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "1", {"text": "I love pizza"})
store.put(("user_123", "memories"), "2", {"text": "I am a plumber"})
def chat(state, *, store: BaseStore):
# Search based on user's last message
items = store.search(
("user_123", "memories"), query=state["messages"][-1].content, limit=2
)
memories = "\n".join(item.value["text"] for item in items)
memories = f"## Memories of user\n{memories}" if memories else ""
response = model.invoke(
[
{"role": "system", "content": f"You are a helpful assistant.\n{memories}"},
*state["messages"],
]
)
return {"messages": [response]}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(chat)
builder.add_edge(START, "chat")
graph = builder.compile(store=store)
for message, metadata in graph.stream(
input={"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "I'm hungry"}]},
stream_mode="messages",
):
print(message.content, end="")
Manage short-term memory
단기 메모리가 활성화된 경우, 긴 대화는 LLM의 컨텍스트 윈도우를 초과할 수 있습니다. 일반적인 해결책은 다음과 같습니다:- 메시지 자르기: 처음 또는 마지막 N개의 메시지 제거 (LLM 호출 전)
- LangGraph state에서 메시지 삭제를 영구적으로 수행
- 메시지 요약: 히스토리의 이전 메시지를 요약하고 요약본으로 대체
- checkpoint 관리를 통해 메시지 히스토리 저장 및 검색
- 사용자 정의 전략 (예: 메시지 필터링 등)
Trim messages
대부분의 LLM은 최대 지원 컨텍스트 윈도우(토큰 단위)를 가지고 있습니다. 메시지를 자를 시점을 결정하는 한 가지 방법은 메시지 히스토리의 토큰을 계산하고 해당 제한에 근접할 때마다 자르는 것입니다. LangChain을 사용하는 경우, trim messages 유틸리티를 사용하여 목록에서 유지할 토큰 수와 경계 처리를 위한strategy(예: 마지막 max_tokens 유지)를 지정할 수 있습니다.
메시지 히스토리를 자르려면 trim_messages 함수를 사용하세요:
Copy
from langchain_core.messages.utils import (
trim_messages,
count_tokens_approximately
)
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
messages = trim_messages(
state["messages"],
strategy="last",
token_counter=count_tokens_approximately,
max_tokens=128,
start_on="human",
end_on=("human", "tool"),
)
response = model.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
...
전체 예제: 메시지 자르기
전체 예제: 메시지 자르기
Copy
from langchain_core.messages.utils import (
trim_messages,
count_tokens_approximately
)
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, MessagesState
model = init_chat_model("anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-5")
summarization_model = model.bind(max_tokens=128)
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
messages = trim_messages(
state["messages"],
strategy="last",
token_counter=count_tokens_approximately,
max_tokens=128,
start_on="human",
end_on=("human", "tool"),
)
response = model.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
graph.invoke({"messages": "hi, my name is bob"}, config)
graph.invoke({"messages": "write a short poem about cats"}, config)
graph.invoke({"messages": "now do the same but for dogs"}, config)
final_response = graph.invoke({"messages": "what's my name?"}, config)
final_response["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
Copy
================================== Ai Message ==================================
Your name is Bob, as you mentioned when you first introduced yourself.
Delete messages
그래프 state에서 메시지를 삭제하여 메시지 히스토리를 관리할 수 있습니다. 이는 특정 메시지를 제거하거나 전체 메시지 히스토리를 지우려는 경우 유용합니다. 그래프 state에서 메시지를 삭제하려면RemoveMessage를 사용할 수 있습니다. RemoveMessage가 작동하려면 MessagesState와 같이 add_messages reducer가 있는 state key를 사용해야 합니다.
특정 메시지를 제거하려면:
Copy
from langchain.messages import RemoveMessage
def delete_messages(state):
messages = state["messages"]
if len(messages) > 2:
# remove the earliest two messages
return {"messages": [RemoveMessage(id=m.id) for m in messages[:2]]}
Copy
from langgraph.graph.message import REMOVE_ALL_MESSAGES
def delete_messages(state):
return {"messages": [RemoveMessage(id=REMOVE_ALL_MESSAGES)]}
메시지를 삭제할 때는 결과 메시지 히스토리가 유효한지 확인하세요. 사용 중인 LLM 제공자의 제한 사항을 확인하세요. 예를 들어:
- 일부 제공자는 메시지 히스토리가
user메시지로 시작하기를 기대합니다 - 대부분의 제공자는 tool call이 있는
assistant메시지 다음에 해당하는tool결과 메시지가 와야 합니다.
전체 예제: 메시지 삭제
전체 예제: 메시지 삭제
Copy
from langchain.messages import RemoveMessage
def delete_messages(state):
messages = state["messages"]
if len(messages) > 2:
# remove the earliest two messages
return {"messages": [RemoveMessage(id=m.id) for m in messages[:2]]}
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
response = model.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": response}
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
builder.add_sequence([call_model, delete_messages])
builder.add_edge(START, "call_model")
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
app = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
for event in app.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi! I'm bob"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
print([(message.type, message.content) for message in event["messages"]])
for event in app.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what's my name?"}]},
config,
stream_mode="values"
):
print([(message.type, message.content) for message in event["messages"]])
Copy
[('human', "hi! I'm bob")]
[('human', "hi! I'm bob"), ('ai', 'Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?')]
[('human', "hi! I'm bob"), ('ai', 'Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?'), ('human', "what's my name?")]
[('human', "hi! I'm bob"), ('ai', 'Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?'), ('human', "what's my name?"), ('ai', 'Your name is Bob.')]
[('human', "what's my name?"), ('ai', 'Your name is Bob.')]
Summarize messages
위에서 보여준 것처럼 메시지를 자르거나 제거하는 것의 문제점은 메시지 큐를 정리하면서 정보를 잃을 수 있다는 것입니다. 이 때문에 일부 애플리케이션은 chat model을 사용하여 메시지 히스토리를 요약하는 보다 정교한 접근 방식의 이점을 얻습니다.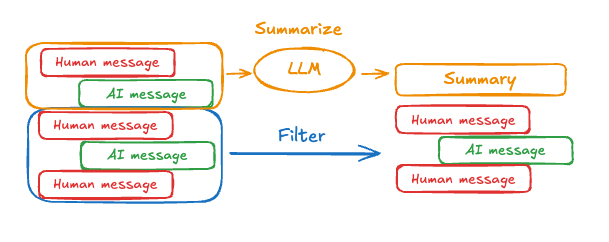 프롬프팅 및 오케스트레이션 로직을 사용하여 메시지 히스토리를 요약할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, LangGraph에서는
프롬프팅 및 오케스트레이션 로직을 사용하여 메시지 히스토리를 요약할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, LangGraph에서는 MessagesState를 확장하여 summary key를 포함할 수 있습니다:
Copy
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
class State(MessagesState):
summary: str
summarize_conversation node는 messages state key에 일정 수의 메시지가 누적된 후 호출될 수 있습니다.
Copy
def summarize_conversation(state: State):
# First, we get any existing summary
summary = state.get("summary", "")
# Create our summarization prompt
if summary:
# A summary already exists
summary_message = (
f"This is a summary of the conversation to date: {summary}\n\n"
"Extend the summary by taking into account the new messages above:"
)
else:
summary_message = "Create a summary of the conversation above:"
# Add prompt to our history
messages = state["messages"] + [HumanMessage(content=summary_message)]
response = model.invoke(messages)
# Delete all but the 2 most recent messages
delete_messages = [RemoveMessage(id=m.id) for m in state["messages"][:-2]]
return {"summary": response.content, "messages": delete_messages}
전체 예제: 메시지 요약
전체 예제: 메시지 요약
Copy
from typing import Any, TypedDict
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.messages import AnyMessage
from langchain_core.messages.utils import count_tokens_approximately
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, MessagesState
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langmem.short_term import SummarizationNode, RunningSummary
model = init_chat_model("anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-5")
summarization_model = model.bind(max_tokens=128)
class State(MessagesState):
context: dict[str, RunningSummary]
class LLMInputState(TypedDict):
summarized_messages: list[AnyMessage]
context: dict[str, RunningSummary]
summarization_node = SummarizationNode(
token_counter=count_tokens_approximately,
model=summarization_model,
max_tokens=256,
max_tokens_before_summary=256,
max_summary_tokens=128,
)
def call_model(state: LLMInputState):
response = model.invoke(state["summarized_messages"])
return {"messages": [response]}
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
builder = StateGraph(State)
builder.add_node(call_model)
builder.add_node("summarize", summarization_node)
builder.add_edge(START, "summarize")
builder.add_edge("summarize", "call_model")
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
# Invoke the graph
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
graph.invoke({"messages": "hi, my name is bob"}, config)
graph.invoke({"messages": "write a short poem about cats"}, config)
graph.invoke({"messages": "now do the same but for dogs"}, config)
final_response = graph.invoke({"messages": "what's my name?"}, config)
final_response["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
print("\nSummary:", final_response["context"]["running_summary"].summary)
context필드에서 실행 중인 요약을 추적합니다
SummarizationNode에서 예상됨).-
call_modelnode에 대한 입력을 필터링하는 데만 사용될 private state를 정의합니다. - 여기서는 요약 node에서 반환된 메시지를 격리하기 위해 private input state를 전달합니다
Copy
================================== Ai Message ==================================
From our conversation, I can see that you introduced yourself as Bob. That's the name you shared with me when we began talking.
Summary: In this conversation, I was introduced to Bob, who then asked me to write a poem about cats. I composed a poem titled "The Mystery of Cats" that captured cats' graceful movements, independent nature, and their special relationship with humans. Bob then requested a similar poem about dogs, so I wrote "The Joy of Dogs," which highlighted dogs' loyalty, enthusiasm, and loving companionship. Both poems were written in a similar style but emphasized the distinct characteristics that make each pet special.
Manage checkpoints
checkpointer에 저장된 정보를 보고 삭제할 수 있습니다.View thread state
- Graph/Functional API
- Checkpointer API
Copy
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1",
# optionally provide an ID for a specific checkpoint,
# otherwise the latest checkpoint is shown
# "checkpoint_id": "1f029ca3-1f5b-6704-8004-820c16b69a5a" #
}
}
graph.get_state(config)
Copy
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob"), AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today?), HumanMessage(content="what's my name?"), AIMessage(content='Your name is Bob.')]}, next=(),
config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-1f5b-6704-8004-820c16b69a5a'}},
metadata={
'source': 'loop',
'writes': {'call_model': {'messages': AIMessage(content='Your name is Bob.')}},
'step': 4,
'parents': {},
'thread_id': '1'
},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:24.680462+00:00',
parent_config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-1790-6b0a-8003-baf965b6a38f'}},
tasks=(),
interrupts=()
)
View the history of the thread
- Graph/Functional API
- Checkpointer API
Copy
config = {
"configurable": {
"thread_id": "1"
}
}
list(graph.get_state_history(config))
Copy
[
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob"), AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?'), HumanMessage(content="what's my name?"), AIMessage(content='Your name is Bob.')]},
next=(),
config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-1f5b-6704-8004-820c16b69a5a'}},
metadata={'source': 'loop', 'writes': {'call_model': {'messages': AIMessage(content='Your name is Bob.')}}, 'step': 4, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:24.680462+00:00',
parent_config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-1790-6b0a-8003-baf965b6a38f'}},
tasks=(),
interrupts=()
),
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob"), AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?'), HumanMessage(content="what's my name?")]},
next=('call_model',),
config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-1790-6b0a-8003-baf965b6a38f'}},
metadata={'source': 'loop', 'writes': None, 'step': 3, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:23.863421+00:00',
parent_config={...}
tasks=(PregelTask(id='8ab4155e-6b15-b885-9ce5-bed69a2c305c', name='call_model', path=('__pregel_pull', 'call_model'), error=None, interrupts=(), state=None, result={'messages': AIMessage(content='Your name is Bob.')}),),
interrupts=()
),
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob"), AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?')]},
next=('__start__',),
config={...},
metadata={'source': 'input', 'writes': {'__start__': {'messages': [{'role': 'user', 'content': "what's my name?"}]}}, 'step': 2, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:23.863173+00:00',
parent_config={...}
tasks=(PregelTask(id='24ba39d6-6db1-4c9b-f4c5-682aeaf38dcd', name='__start__', path=('__pregel_pull', '__start__'), error=None, interrupts=(), state=None, result={'messages': [{'role': 'user', 'content': "what's my name?"}]}),),
interrupts=()
),
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob"), AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?')]},
next=(),
config={...},
metadata={'source': 'loop', 'writes': {'call_model': {'messages': AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?')}}, 'step': 1, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:23.862295+00:00',
parent_config={...}
tasks=(),
interrupts=()
),
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content="hi! I'm bob")]},
next=('call_model',),
config={...},
metadata={'source': 'loop', 'writes': None, 'step': 0, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:22.278960+00:00',
parent_config={...}
tasks=(PregelTask(id='8cbd75e0-3720-b056-04f7-71ac805140a0', name='call_model', path=('__pregel_pull', 'call_model'), error=None, interrupts=(), state=None, result={'messages': AIMessage(content='Hi Bob! How are you doing today? Is there anything I can help you with?')}),),
interrupts=()
),
StateSnapshot(
values={'messages': []},
next=('__start__',),
config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f029ca3-0870-6ce2-bfff-1f3f14c3e565'}},
metadata={'source': 'input', 'writes': {'__start__': {'messages': [{'role': 'user', 'content': "hi! I'm bob"}]}}, 'step': -1, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'},
created_at='2025-05-05T16:01:22.277497+00:00',
parent_config=None,
tasks=(PregelTask(id='d458367b-8265-812c-18e2-33001d199ce6', name='__start__', path=('__pregel_pull', '__start__'), error=None, interrupts=(), state=None, result={'messages': [{'role': 'user', 'content': "hi! I'm bob"}]}),),
interrupts=()
)
]
Delete all checkpoints for a thread
Copy
thread_id = "1"
checkpointer.delete_thread(thread_id)
Prebuilt memory tools
LangMem은 에이전트에서 장기 메모리를 관리하기 위한 도구를 제공하는 LangChain 유지 관리 라이브러리입니다. 사용 예제는 LangMem 문서를 참조하세요.Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

