목표
이 예제에서는 GitHub 이슈를 제목을 기반으로 분류하는 봇을 만들 것입니다. 제목을 입력받아 여러 다른 클래스 중 하나로 분류합니다. 그런 다음 사용자 피드백을 수집하기 시작하고 이를 사용하여 classifier의 성능을 개선할 것입니다.시작하기
시작하려면 먼저 모든 trace를 특정 프로젝트로 보내도록 설정합니다. 환경 변수를 설정하여 이를 수행할 수 있습니다:자동화 설정하기
이제 어떤 형태의 피드백이 있는 예제를 dataset으로 이동시키는 자동화를 설정할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 피드백과 부정적인 피드백에 대해 각각 하나씩 두 개의 자동화를 설정할 것입니다. 첫 번째는 긍정적인 피드백이 있는 모든 run을 자동으로 dataset에 추가합니다. 이것의 논리는 긍정적인 피드백이 있는 모든 run을 향후 반복에서 좋은 예제로 사용할 수 있다는 것입니다. 이 데이터를 추가할classifier-github-issues라는 dataset을 만들어 봅시다.
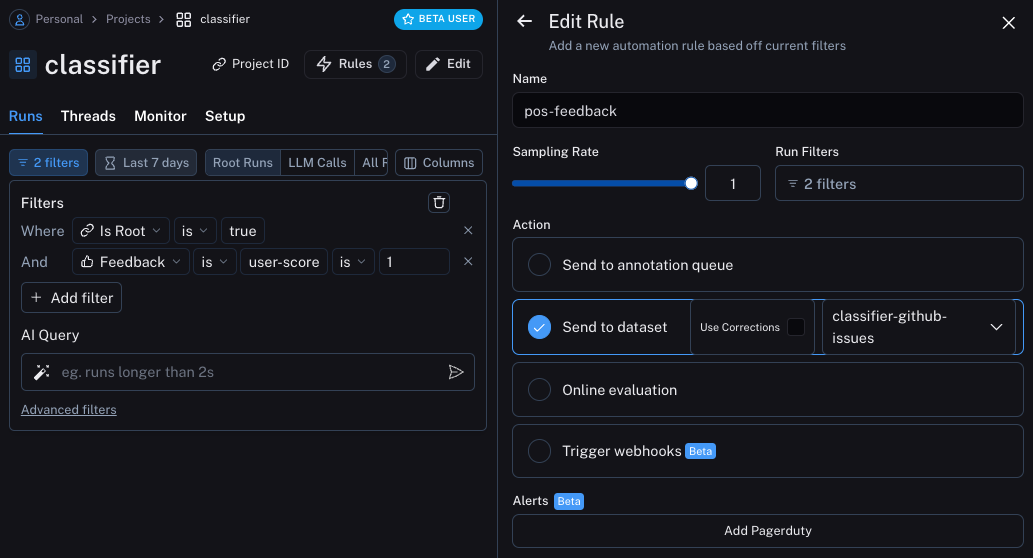 두 번째는 수정이 있는 모든 run을 가져와 webhook을 사용하여 dataset에 추가합니다. 이 webhook을 생성할 때 “Use Corrections” 옵션을 선택합니다. 이 옵션은 run에서 dataset을 생성할 때 run의 출력을 datapoint의 정답 출력으로 사용하는 대신 수정 사항을 사용하도록 합니다.
두 번째는 수정이 있는 모든 run을 가져와 webhook을 사용하여 dataset에 추가합니다. 이 webhook을 생성할 때 “Use Corrections” 옵션을 선택합니다. 이 옵션은 run에서 dataset을 생성할 때 run의 출력을 datapoint의 정답 출력으로 사용하는 대신 수정 사항을 사용하도록 합니다.

애플리케이션 업데이트하기
이제 run을 보내고 있는 dataset을 가져오도록 코드를 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 가져온 후에는 예제가 포함된 문자열을 만들 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 이 문자열을 prompt의 일부로 넣을 수 있습니다!documentation으로 분류되어야 한다는 것을 올바르게 학습하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
예제에 대한 의미론적 검색
추가로 할 수 있는 한 가지는 의미론적으로 가장 유사한 예제만 사용하는 것입니다. 이것은 많은 예제를 구축하기 시작할 때 유용합니다. 이를 위해 먼저k개의 가장 유사한 예제를 찾는 예제를 정의할 수 있습니다:
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

