SQL 데이터베이스의 Q&A 시스템을 구축하려면 모델이 생성한 SQL 쿼리를 실행해야 합니다. 이를 수행하는 데는 본질적인 위험이 있습니다. 데이터베이스 연결 권한이 항상 에이전트의 필요에 따라 가능한 한 좁게 범위가 지정되어 있는지 확인하세요. 이는 모델 기반 시스템 구축의 위험을 완화하지만 제거하지는 못합니다.
개념
다음 개념을 다룰 것입니다:- SQL 데이터베이스에서 읽기 위한 Tools
- state, node, edge, conditional edge를 포함한 LangGraph Graph API
- Human-in-the-loop 프로세스
설정
설치
LangSmith
체인이나 에이전트 내부에서 무슨 일이 일어나는지 검사하려면 LangSmith를 설정하세요. 그런 다음 다음 환경 변수를 설정하세요:1. LLM 선택
tool-calling을 지원하는 모델을 선택하세요:- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Azure
- Google Gemini
- AWS Bedrock
아래 예제에 표시된 출력은 OpenAI를 사용했습니다.
2. 데이터베이스 구성
이 튜토리얼을 위해 SQLite database를 생성할 것입니다. SQLite는 설정하고 사용하기 쉬운 경량 데이터베이스입니다. 디지털 미디어 스토어를 나타내는 샘플 데이터베이스인chinook 데이터베이스를 로드할 것입니다.
편의를 위해 공개 GCS 버킷에 데이터베이스(Chinook.db)를 호스팅했습니다.
langchain_community 패키지에서 사용 가능한 편리한 SQL 데이터베이스 래퍼를 사용할 것입니다. 이 래퍼는 SQL 쿼리를 실행하고 결과를 가져오는 간단한 인터페이스를 제공합니다:
3. 데이터베이스 상호 작용을 위한 도구 추가
데이터베이스와 상호 작용하기 위해langchain_community 패키지에서 사용 가능한 SQLDatabase 래퍼를 사용하세요. 이 래퍼는 SQL 쿼리를 실행하고 결과를 가져오는 간단한 인터페이스를 제공합니다:
4. 애플리케이션 단계 정의
다음 단계를 위한 전용 노드를 구성합니다:- DB 테이블 나열
- “get schema” 도구 호출
- 쿼리 생성
- 쿼리 확인
5. 에이전트 구현
이제 Graph API를 사용하여 이러한 단계를 워크플로우로 조립할 수 있습니다. 쿼리 생성 단계에서 conditional edge를 정의하여 쿼리가 생성되면 query checker로 라우팅하거나, LLM이 쿼리에 대한 응답을 전달한 것과 같이 tool call이 없으면 종료합니다.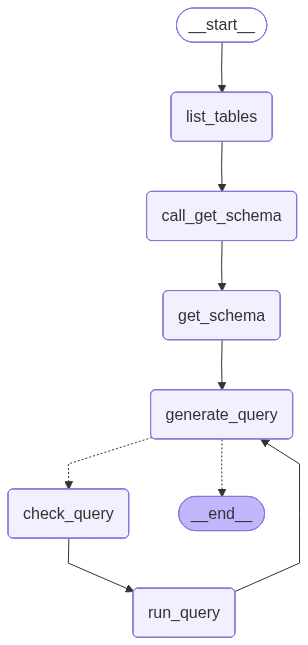 이제 그래프를 호출할 수 있습니다:
이제 그래프를 호출할 수 있습니다:
위 실행에 대한 LangSmith trace를 참조하세요.
6. Human-in-the-loop 검토 구현
에이전트의 SQL 쿼리가 실행되기 전에 의도하지 않은 작업이나 비효율성이 있는지 확인하는 것이 현명할 수 있습니다. 여기서는 LangGraph의 human-in-the-loop 기능을 활용하여 SQL 쿼리를 실행하기 전에 실행을 일시 중지하고 사람의 검토를 기다립니다. LangGraph의 persistence layer를 사용하면 실행을 무기한으로(또는 적어도 persistence layer가 살아있는 동안) 일시 중지할 수 있습니다. 사람의 입력을 받는 노드에서sql_db_query 도구를 래핑해 보겠습니다. interrupt 함수를 사용하여 이를 구현할 수 있습니다. 아래에서는 tool call을 승인하거나, 인수를 편집하거나, 사용자 피드백을 제공하기 위한 입력을 허용합니다.
위 구현은 더 광범위한 human-in-the-loop 가이드의 tool interrupt example을 따릅니다. 자세한 내용과 대안은 해당 가이드를 참조하세요.
다음 단계
LangSmith를 사용하여 이와 같은 SQL 에이전트를 포함한 LangGraph 애플리케이션을 평가하는 방법은 Evaluate a graph 가이드를 확인하세요.Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

