개요
Agent(또는 모든 LLM 애플리케이션)를 구축할 때 가장 어려운 부분은 충분히 신뢰할 수 있게 만드는 것입니다. 프로토타입에서는 작동할 수 있지만, 실제 사용 사례에서는 종종 실패합니다.Agent가 실패하는 이유는 무엇인가요?
Agent가 실패할 때, 일반적으로 agent 내부의 LLM 호출이 잘못된 작업을 수행하거나 예상한 대로 작동하지 않았기 때문입니다. LLM은 두 가지 이유 중 하나로 실패합니다:- 기본 LLM이 충분히 유능하지 않음
- “올바른” context가 LLM에 전달되지 않음
Context engineering이 처음이신가요? 개념 개요에서 시작하여 다양한 유형의 context와 사용 시기를 이해하세요.
Agent loop
일반적인 agent loop는 두 가지 주요 단계로 구성됩니다:- Model call - prompt와 사용 가능한 tool로 LLM을 호출하고, 응답 또는 tool 실행 요청을 반환합니다
- Tool execution - LLM이 요청한 tool을 실행하고, tool 결과를 반환합니다
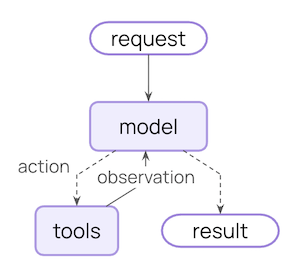
제어할 수 있는 것
신뢰할 수 있는 agent를 구축하려면 agent loop의 각 단계에서 발생하는 일과 단계 사이에 발생하는 일을 제어해야 합니다.| Context 유형 | 제어하는 것 | Transient 또는 Persistent |
|---|---|---|
| Model Context | Model call에 들어가는 것 (지시사항, 메시지 기록, tool, 응답 형식) | Transient |
| Tool Context | Tool이 액세스하고 생성할 수 있는 것 (state, store, runtime context에 대한 읽기/쓰기) | Persistent |
| Life-cycle Context | Model과 tool call 사이에 발생하는 것 (요약, guardrail, 로깅 등) | Persistent |
Transient context
LLM이 단일 호출에서 보는 것입니다. State에 저장된 내용을 변경하지 않고 메시지, tool 또는 prompt를 수정할 수 있습니다.
Persistent context
턴 전체에 걸쳐 state에 저장되는 것입니다. Life-cycle hook과 tool 쓰기는 이것을 영구적으로 수정합니다.
데이터 소스
이 과정 전반에 걸쳐 agent는 다양한 데이터 소스에 액세스(읽기/쓰기)합니다:| 데이터 소스 | 다른 이름 | 범위 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runtime Context | 정적 구성 | 대화 범위 | 사용자 ID, API key, 데이터베이스 연결, 권한, 환경 설정 |
| State | 단기 메모리 | 대화 범위 | 현재 메시지, 업로드된 파일, 인증 상태, tool 결과 |
| Store | 장기 메모리 | 대화 간 | 사용자 선호도, 추출된 인사이트, 메모리, 과거 데이터 |
작동 방식
LangChain middleware는 LangChain을 사용하는 개발자에게 context engineering을 실용적으로 만드는 기본 메커니즘입니다. Middleware를 사용하면 agent 생명주기의 모든 단계에 연결하여 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다:- Context 업데이트
- Agent 생명주기의 다른 단계로 이동
Model Context
각 model call에 들어가는 것을 제어합니다 - 지시사항, 사용 가능한 tool, 사용할 model, 출력 형식. 이러한 결정은 신뢰성과 비용에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다.System Prompt
개발자가 LLM에게 제공하는 기본 지시사항.
Messages
LLM에 전송되는 전체 메시지 목록(대화 기록).
Tools
Agent가 작업을 수행하기 위해 액세스할 수 있는 유틸리티.
Model
호출될 실제 model(구성 포함).
Response Format
Model의 최종 응답에 대한 스키마 사양.
System Prompt
System prompt는 LLM의 동작과 기능을 설정합니다. 다른 사용자, context 또는 대화 단계에는 다른 지시사항이 필요합니다. 성공적인 agent는 메모리, 선호도 및 구성을 활용하여 대화의 현재 상태에 적합한 지시사항을 제공합니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
State에서 메시지 수 또는 대화 context에 액세스:
Messages
Message는 LLM에 전송되는 prompt를 구성합니다. LLM이 올바른 정보를 가지고 잘 응답할 수 있도록 메시지의 내용을 관리하는 것이 중요합니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
현재 쿼리와 관련이 있을 때 State에서 업로드된 파일 context를 주입:
Transient vs Persistent 메시지 업데이트:위의 예제는
wrap_model_call을 사용하여 transient 업데이트를 수행합니다 - state에 저장된 내용을 변경하지 않고 단일 호출에 대해 model에 전송되는 메시지를 수정합니다.State를 수정하는 persistent 업데이트(예: Life-cycle Context의 요약 예제)의 경우, before_model 또는 after_model과 같은 life-cycle hook을 사용하여 대화 기록을 영구적으로 업데이트하세요. 자세한 내용은 middleware 문서를 참조하세요.Tools
Tool을 사용하면 model이 데이터베이스, API 및 외부 시스템과 상호 작용할 수 있습니다. Tool을 정의하고 선택하는 방법은 model이 작업을 효과적으로 완료할 수 있는지 여부에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다.Tool 정의
각 tool에는 명확한 이름, 설명, 인수 이름 및 인수 설명이 필요합니다. 이것들은 단순한 메타데이터가 아닙니다—tool을 언제 어떻게 사용할지에 대한 model의 추론을 안내합니다.Tool 선택
모든 tool이 모든 상황에 적합한 것은 아닙니다. 너무 많은 tool은 model을 압도하고(context 과부하) 오류를 증가시킬 수 있습니다; 너무 적으면 기능이 제한됩니다. 동적 tool 선택은 인증 상태, 사용자 권한, feature flag 또는 대화 단계에 따라 사용 가능한 toolset을 조정합니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
특정 대화 이정표 이후에만 고급 tool 활성화:
Model
다른 model은 다른 강점, 비용 및 context window를 가지고 있습니다. 당면한 작업에 적합한 model을 선택하세요. 이는 agent 실행 중에 변경될 수 있습니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
State의 대화 길이에 따라 다른 model 사용:
Response Format
구조화된 출력은 비구조화된 텍스트를 검증된 구조화된 데이터로 변환합니다. 특정 필드를 추출하거나 다운스트림 시스템에 대한 데이터를 반환할 때 자유 형식 텍스트는 충분하지 않습니다. 작동 방식: 응답 형식으로 스키마를 제공하면 model의 최종 응답이 해당 스키마를 준수하도록 보장됩니다. Agent는 model이 tool 호출을 완료할 때까지 model / tool 호출 loop를 실행한 다음 최종 응답이 제공된 형식으로 강제 변환됩니다.형식 정의
스키마 정의는 model을 안내합니다. 필드 이름, 유형 및 설명은 출력이 준수해야 하는 형식을 정확히 지정합니다.형식 선택
동적 응답 형식 선택은 사용자 선호도, 대화 단계 또는 역할에 따라 스키마를 조정합니다—초기에는 간단한 형식을 반환하고 복잡성이 증가함에 따라 상세한 형식을 반환합니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
대화 state에 따라 구조화된 출력 구성:
Tool Context
Tool은 context를 읽고 쓰는 점에서 특별합니다. 가장 기본적인 경우, tool이 실행될 때 LLM의 요청 매개변수를 받고 tool 메시지를 반환합니다. Tool은 작업을 수행하고 결과를 생성합니다. Tool은 또한 model이 작업을 수행하고 완료할 수 있도록 하는 중요한 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다.읽기
대부분의 실제 tool은 LLM의 매개변수 이상이 필요합니다. 데이터베이스 쿼리를 위한 사용자 ID, 외부 서비스를 위한 API key 또는 결정을 내리기 위한 현재 세션 state가 필요합니다. Tool은 이 정보에 액세스하기 위해 state, store 및 runtime context에서 읽습니다.- State
- Store
- Runtime Context
현재 세션 정보를 확인하기 위해 State에서 읽기:
쓰기
Tool 결과는 agent가 주어진 작업을 완료하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. Tool은 결과를 model에 직접 반환하고 agent의 메모리를 업데이트하여 향후 단계에서 중요한 context를 사용할 수 있도록 할 수 있습니다.- State
- Store
Command를 사용하여 세션별 정보를 추적하기 위해 State에 쓰기:
Life-cycle Context
핵심 agent 단계 사이에 발생하는 것을 제어합니다 - 요약, guardrail 및 로깅과 같은 교차 관심사를 구현하기 위해 데이터 흐름을 가로챕니다. Model Context 및 Tool Context에서 보았듯이, middleware는 context engineering을 실용적으로 만드는 메커니즘입니다. Middleware를 사용하면 agent 생명주기의 모든 단계에 연결하여 다음 중 하나를 수행할 수 있습니다:- Context 업데이트 - 변경 사항을 지속하고, 대화 기록을 업데이트하거나, 인사이트를 저장하기 위해 state 및 store를 수정합니다
- 생명주기에서 이동 - context에 따라 agent 주기의 다른 단계로 이동합니다(예: 조건이 충족되면 tool 실행을 건너뛰고, 수정된 context로 model call을 반복)
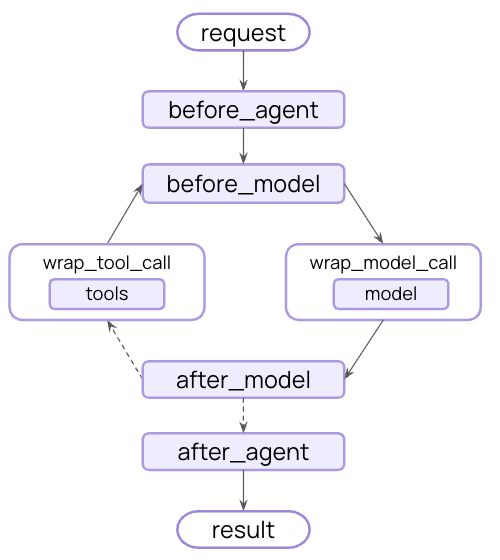
예제: 요약
가장 일반적인 life-cycle 패턴 중 하나는 대화 기록이 너무 길어질 때 자동으로 압축하는 것입니다. Model Context에 표시된 transient 메시지 트리밍과 달리, 요약은 state를 영구적으로 업데이트합니다 - 이전 메시지를 향후 모든 턴에 대해 저장되는 요약으로 영구적으로 대체합니다. LangChain은 이를 위한 내장 middleware를 제공합니다:SummarizationMiddleware가 자동으로:
- 별도의 LLM 호출을 사용하여 이전 메시지를 요약합니다
- State에서 요약 메시지로 대체합니다(영구적으로)
- Context를 위해 최근 메시지를 그대로 유지합니다
내장 middleware의 전체 목록, 사용 가능한 hook 및 사용자 정의 middleware를 만드는 방법은 Middleware 문서를 참조하세요.
모범 사례
- 간단하게 시작 - 정적 prompt와 tool로 시작하고, 필요할 때만 동적 기능을 추가하세요
- 점진적으로 테스트 - 한 번에 하나의 context engineering 기능을 추가하세요
- 성능 모니터링 - Model call, 토큰 사용량 및 지연 시간을 추적하세요
- 내장 middleware 사용 -
SummarizationMiddleware,LLMToolSelectorMiddleware등을 활용하세요 - Context 전략 문서화 - 어떤 context가 전달되고 있는지, 그 이유를 명확히 하세요
- Transient vs persistent 이해: Model context 변경은 transient(호출당)이며, life-cycle context 변경은 state에 지속됩니다
관련 리소스
- Context 개념 개요 - Context 유형과 사용 시기 이해
- Middleware - 완전한 middleware 가이드
- Tools - Tool 생성 및 context 액세스
- Memory - 단기 및 장기 메모리 패턴
- Agents - 핵심 agent 개념
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

