개요
LLM이 가능하게 하는 가장 강력한 애플리케이션 중 하나는 정교한 질의응답(Q&A) 챗봇입니다. 이는 특정 소스 정보에 대한 질문에 답변할 수 있는 애플리케이션입니다. 이러한 애플리케이션은 Retrieval Augmented Generation 또는 RAG로 알려진 기술을 사용합니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 비구조화된 텍스트 데이터 소스에 대한 간단한 Q&A 애플리케이션을 구축하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 다음을 시연할 것입니다:- 간단한 tool로 검색을 실행하는 RAG 에이전트. 이는 범용적으로 좋은 구현입니다.
- 쿼리당 단일 LLM 호출만 사용하는 2단계 RAG 체인. 이는 간단한 쿼리에 대한 빠르고 효과적인 방법입니다.
개념
다음 개념을 다룰 것입니다:- Indexing: 소스에서 데이터를 수집하고 인덱싱하는 파이프라인. 이는 일반적으로 별도의 프로세스에서 발생합니다.
- Retrieval and generation: 실제 RAG 프로세스로, 런타임에 사용자 쿼리를 받아 인덱스에서 관련 데이터를 검색한 다음 이를 모델에 전달합니다.
이 튜토리얼의 인덱싱 부분은 대부분 semantic search 튜토리얼을 따릅니다.데이터가 이미 검색 가능한 경우(즉, 검색을 실행하는 함수가 있는 경우) 또는 해당 튜토리얼의 내용에 익숙한 경우 retrieval and generation 섹션으로 건너뛰어도 됩니다.
미리보기
이 가이드에서는 웹사이트 콘텐츠에 대한 질문에 답변하는 앱을 만들 것입니다. 사용할 특정 웹사이트는 Lilian Weng의 LLM Powered Autonomous Agents 블로그 게시물로, 게시물의 내용에 대해 질문할 수 있습니다. 약 40줄의 코드로 간단한 인덱싱 파이프라인과 RAG 체인을 만들 수 있습니다. 전체 코드 스니펫은 아래를 참조하세요:전체 코드 스니펫 펼치기
전체 코드 스니펫 펼치기
설정
설치
이 튜토리얼에는 다음 langchain 종속성이 필요합니다:LangSmith
LangChain으로 구축하는 많은 애플리케이션에는 여러 LLM 호출이 포함된 여러 단계가 포함됩니다. 이러한 애플리케이션이 복잡해질수록 체인이나 에이전트 내부에서 정확히 무슨 일이 일어나고 있는지 검사할 수 있는 것이 중요해집니다. 이를 수행하는 가장 좋은 방법은 LangSmith를 사용하는 것입니다. 위 링크에서 가입한 후 trace 로깅을 시작하려면 환경 변수를 설정해야 합니다:구성 요소
LangChain의 통합 제품군에서 세 가지 구성 요소를 선택해야 합니다. chat model을 선택하세요:- OpenAI
- Anthropic
- Azure
- Google Gemini
- AWS Bedrock
embeddings model을 선택하세요:
- OpenAI
- Azure
- Google Gemini
- Google Vertex
- AWS
- HuggingFace
- Ollama
- Cohere
- MistralAI
- Nomic
- NVIDIA
- Voyage AI
- IBM watsonx
- Fake
vector store를 선택하세요:
- In-memory
- AstraDB
- Chroma
- FAISS
- Milvus
- MongoDB
- PGVector
- PGVectorStore
- Pinecone
- Qdrant
1. Indexing
이 섹션은 semantic search 튜토리얼의 내용을 축약한 버전입니다.데이터가 이미 인덱싱되어 검색 가능한 경우(즉, 검색을 실행하는 함수가 있는 경우) 또는 document loaders, embeddings, vector stores에 익숙한 경우 retrieval and generation에 대한 다음 섹션으로 건너뛰어도 됩니다.
- Load: 먼저 데이터를 로드해야 합니다. 이는 Document Loaders로 수행됩니다.
- Split: Text splitters는 큰
Documents를 더 작은 청크로 나눕니다. 이는 데이터를 인덱싱하고 모델에 전달하는 데 유용합니다. 큰 청크는 검색하기 어렵고 모델의 제한된 context window에 맞지 않기 때문입니다. - Store: 나중에 검색할 수 있도록 분할된 데이터를 저장하고 인덱싱할 장소가 필요합니다. 이는 종종 VectorStore와 Embeddings 모델을 사용하여 수행됩니다.
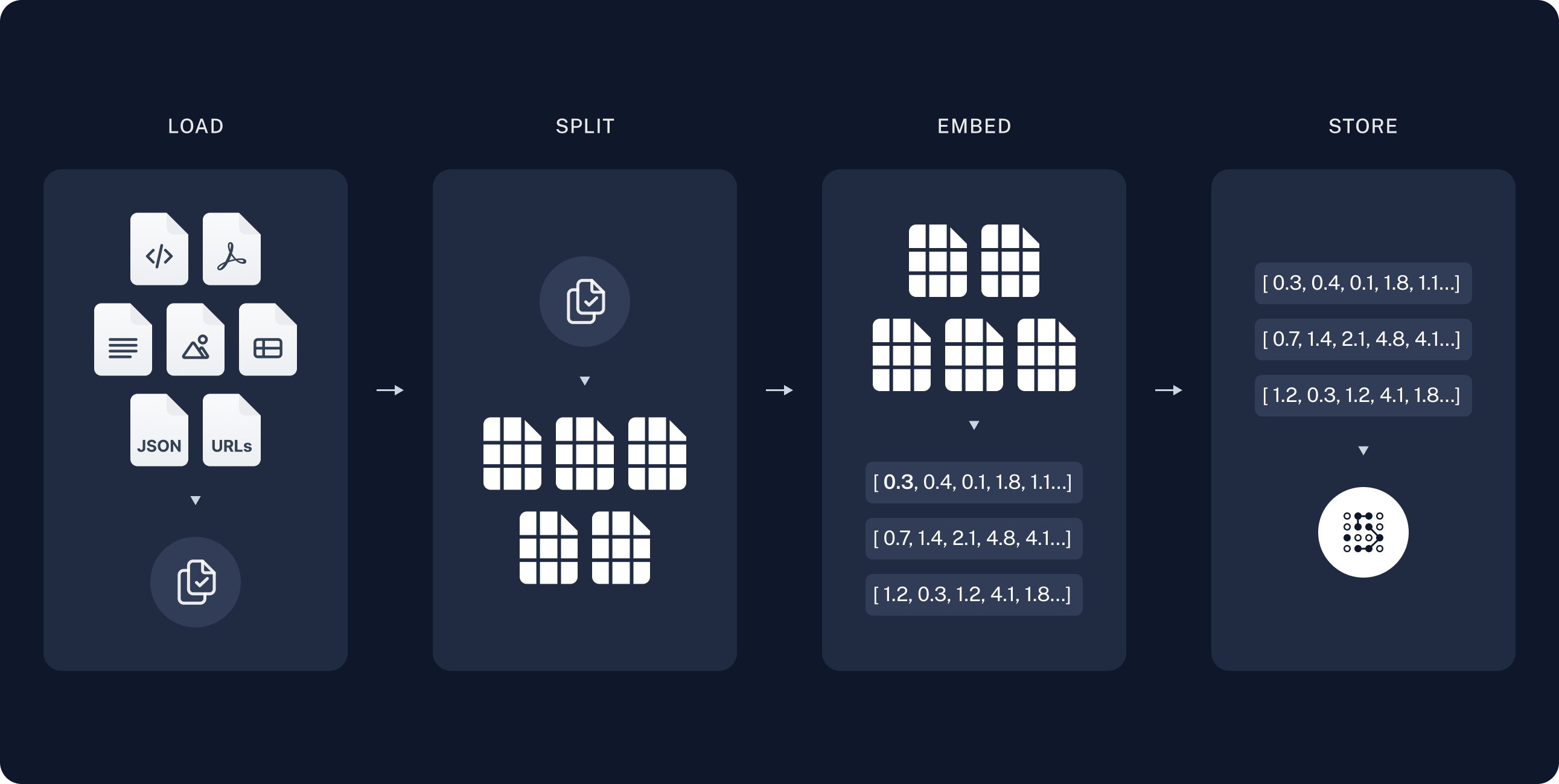
문서 로드
먼저 블로그 게시물 내용을 로드해야 합니다. 이를 위해 DocumentLoaders를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이는 소스에서 데이터를 로드하고 Document 객체 목록을 반환하는 객체입니다. 이 경우WebBaseLoader를 사용합니다. 이는 urllib을 사용하여 웹 URL에서 HTML을 로드하고 BeautifulSoup을 사용하여 텍스트로 파싱합니다. bs_kwargs를 통해 BeautifulSoup 파서에 매개변수를 전달하여 HTML -> 텍스트 파싱을 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다(BeautifulSoup 문서 참조). 이 경우 “post-content”, “post-title” 또는 “post-header” 클래스가 있는 HTML 태그만 관련이 있으므로 다른 모든 태그를 제거합니다.
DocumentLoader: 소스에서 데이터를 Documents 목록으로 로드하는 객체.
- 통합: 선택할 수 있는 160개 이상의 통합.
BaseLoader: 기본 인터페이스에 대한 API 참조.
문서 분할
로드된 문서는 42,000자가 넘어 많은 모델의 context window에 맞지 않습니다. 전체 게시물을 context window에 맞출 수 있는 모델의 경우에도 매우 긴 입력에서 정보를 찾는 데 어려움을 겪을 수 있습니다. 이를 처리하기 위해Document를 embedding 및 vector 저장을 위한 청크로 분할합니다. 이렇게 하면 런타임에 블로그 게시물의 가장 관련성 높은 부분만 검색하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
semantic search 튜토리얼에서와 같이 RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter를 사용합니다. 이는 각 청크가 적절한 크기가 될 때까지 새 줄과 같은 일반적인 구분 기호를 사용하여 문서를 재귀적으로 분할합니다. 이는 일반 텍스트 사용 사례에 권장되는 text splitter입니다.
TextSplitter: Document 객체 목록을 저장 및 검색을 위한 더 작은 청크로 분할하는 객체.
문서 저장
이제 런타임에 검색할 수 있도록 66개의 텍스트 청크를 인덱싱해야 합니다. semantic search 튜토리얼에 따라 각 문서 분할의 내용을 embed하고 이러한 embedding을 vector store에 삽입하는 접근 방식을 사용합니다. 입력 쿼리가 주어지면 vector 검색을 사용하여 관련 문서를 검색할 수 있습니다. 튜토리얼 시작 부분에서 선택한 vector store 및 embeddings model을 사용하여 단일 명령으로 모든 문서 분할을 embed하고 저장할 수 있습니다.Embeddings: 텍스트를 embedding으로 변환하는 데 사용되는 text embedding model의 래퍼.
VectorStore: embedding을 저장하고 쿼리하는 데 사용되는 vector database의 래퍼.
이것으로 파이프라인의 Indexing 부분이 완료됩니다. 이 시점에서 블로그 게시물의 청크된 내용을 포함하는 쿼리 가능한 vector store가 있습니다. 사용자 질문이 주어지면 이상적으로 질문에 답변하는 블로그 게시물의 스니펫을 반환할 수 있어야 합니다.
2. Retrieval and Generation
RAG 애플리케이션은 일반적으로 다음과 같이 작동합니다:- Retrieve: 사용자 입력이 주어지면 Retriever를 사용하여 저장소에서 관련 분할을 검색합니다.
- Generate: 모델이 질문과 검색된 데이터를 모두 포함하는 프롬프트를 사용하여 답변을 생성합니다.
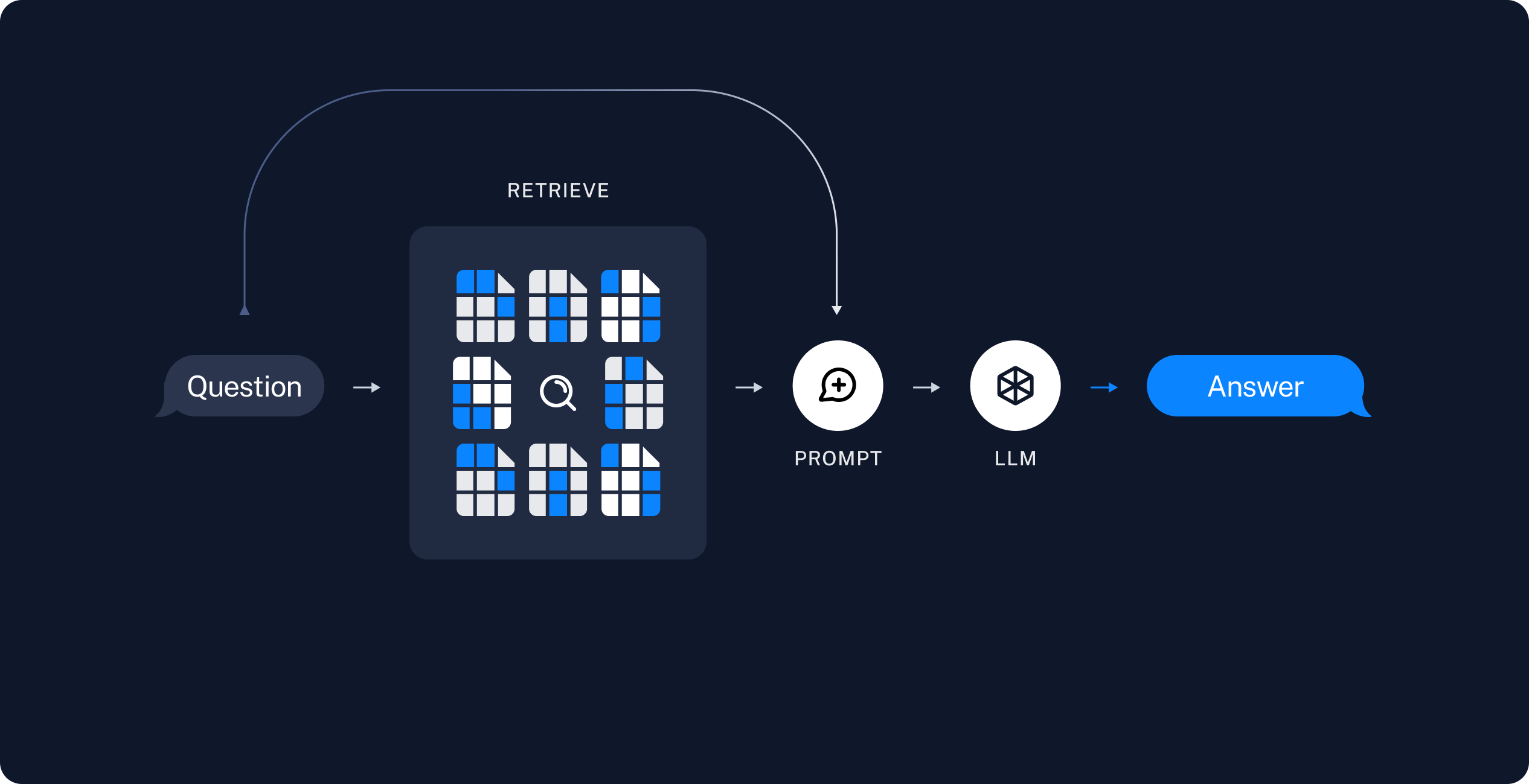 이제 실제 애플리케이션 로직을 작성해 보겠습니다. 사용자 질문을 받아 해당 질문과 관련된 문서를 검색하고, 검색된 문서와 초기 질문을 모델에 전달하여 답변을 반환하는 간단한 애플리케이션을 만들고자 합니다.
다음을 시연할 것입니다:
이제 실제 애플리케이션 로직을 작성해 보겠습니다. 사용자 질문을 받아 해당 질문과 관련된 문서를 검색하고, 검색된 문서와 초기 질문을 모델에 전달하여 답변을 반환하는 간단한 애플리케이션을 만들고자 합니다.
다음을 시연할 것입니다:
- 간단한 tool로 검색을 실행하는 RAG 에이전트. 이는 범용적으로 좋은 구현입니다.
- 쿼리당 단일 LLM 호출만 사용하는 2단계 RAG 체인. 이는 간단한 쿼리에 대한 빠르고 효과적인 방법입니다.
RAG 에이전트
RAG 애플리케이션의 한 가지 형태는 정보를 검색하는 tool이 있는 간단한 에이전트입니다. vector store를 래핑하는 tool을 구현하여 최소한의 RAG 에이전트를 조립할 수 있습니다:여기서는 tool decorator를 사용하여 각 ToolMessage에 원시 문서를 artifacts로 첨부하도록 tool을 구성합니다. 이를 통해 모델로 전송되는 문자열화된 표현과 별도로 애플리케이션에서 문서 메타데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
Retrieval tool은 위 예제와 같이 단일 문자열
query 인수로 제한되지 않습니다. 인수를 추가하여 LLM이 추가 검색 매개변수를 지정하도록 강제할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 카테고리:- task decomposition을 위한 표준 방법을 검색하기 위한 쿼리를 생성합니다;
- 답변을 받은 후 그것의 일반적인 확장을 검색하기 위한 두 번째 쿼리를 생성합니다;
- 필요한 모든 컨텍스트를 받은 후 질문에 답변합니다.
LangGraph 프레임워크를 직접 사용하여 더 깊은 수준의 제어 및 사용자 정의를 추가할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 문서 관련성을 평가하고 검색 쿼리를 다시 작성하는 단계를 추가할 수 있습니다. 더 고급 형태는 LangGraph의 Agentic RAG 튜토리얼을 확인하세요.
RAG 체인
위의 agentic RAG 형태에서는 LLM이 사용자 쿼리에 답변하는 데 도움이 되는 tool call을 생성하는 데 재량을 사용하도록 허용합니다. 이는 범용적으로 좋은 솔루션이지만 몇 가지 트레이드오프가 있습니다:| ✅ 장점 | ⚠️ 단점 |
|---|---|
| 필요할 때만 검색 – LLM은 불필요한 검색을 트리거하지 않고 인사말, 후속 질문 및 간단한 쿼리를 처리할 수 있습니다. | 두 번의 추론 호출 – 검색이 수행되면 쿼리를 생성하기 위한 한 번의 호출과 최종 응답을 생성하기 위한 또 다른 호출이 필요합니다. |
컨텍스트 검색 쿼리 – 검색을 query 입력이 있는 tool로 처리함으로써 LLM은 대화 컨텍스트를 통합하는 자체 쿼리를 작성합니다. | 제어 감소 – LLM은 실제로 필요할 때 검색을 건너뛰거나 불필요할 때 추가 검색을 실행할 수 있습니다. |
| 여러 검색 허용 – LLM은 단일 사용자 쿼리를 지원하기 위해 여러 검색을 실행할 수 있습니다. |
소스 문서 반환
소스 문서 반환
위의 RAG 체인은 해당 실행에 대한 단일 system message에 검색된 컨텍스트를 통합합니다.agentic RAG 형태에서와 같이 때때로 문서 메타데이터에 액세스하기 위해 애플리케이션 상태에 원시 소스 문서를 포함하고 싶을 때가 있습니다. 2단계 체인의 경우 다음을 수행하여 이를 수행할 수 있습니다:
- 검색된 문서를 저장하기 위해 상태에 키 추가
- 해당 키를 채우기 위해 pre-model hook을 통해 새 노드 추가(컨텍스트 주입도 함께)
다음 단계
이제create_agent를 통해 간단한 RAG 애플리케이션을 구현했으므로 새로운 기능을 쉽게 통합하고 더 깊이 들어갈 수 있습니다:
- 반응형 사용자 경험을 위해 token 및 기타 정보 스트리밍
- 다중 턴 상호 작용을 지원하기 위해 대화 메모리 추가
- 대화 스레드 간 메모리를 지원하기 위해 장기 메모리 추가
- 구조화된 응답 추가
- LangSmith Deployments로 애플리케이션 배포
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

