사전 요구 사항
이 튜토리얼을 시작하기 전에 첫 번째 튜토리얼의 봇이 오류 없이 실행되고 있는지 확인하세요.1. 리소스 authorization 추가
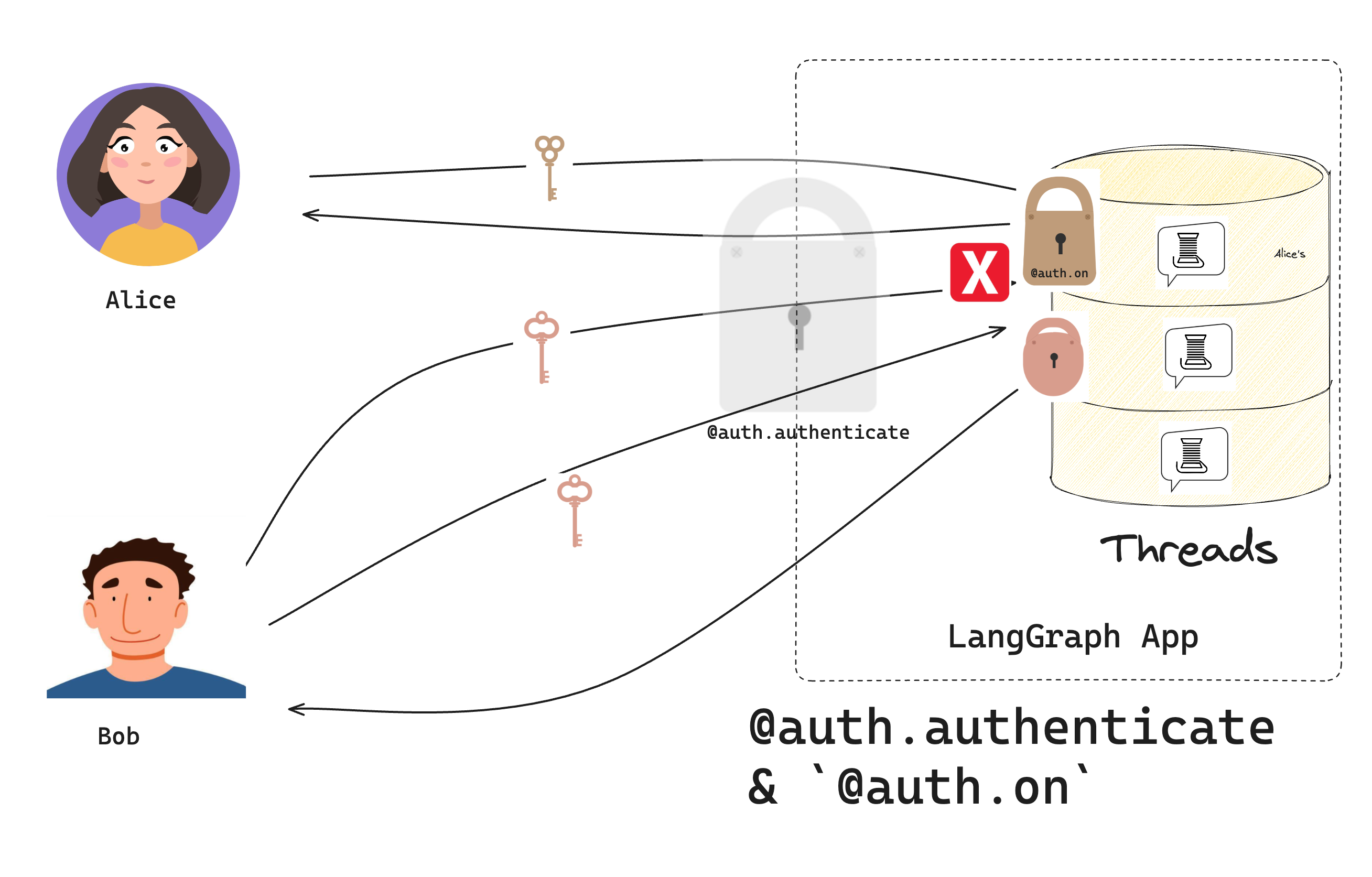
지난 튜토리얼에서Auth 객체를 사용하여 authentication 함수를 등록했으며, LangSmith는 이를 사용하여 들어오는 요청의 bearer token을 검증합니다. 이제 authorization handler를 등록하는 데 사용할 것입니다.
Authorization handler는 authentication이 성공한 후에 실행되는 함수입니다. 이러한 handler는 리소스에 메타데이터(예: 소유자)를 추가하고 각 사용자가 볼 수 있는 내용을 필터링할 수 있습니다.
src/security/auth.py를 업데이트하고 모든 요청에서 실행될 authorization handler를 추가하세요:
src/security/auth.py
ctx(AuthContext): 현재user, 사용자의permissions,resource(“threads”, “crons”, “assistants”), 그리고 수행 중인action(“create”, “read”, “update”, “delete”, “search”, “create_run”)에 대한 정보를 포함합니다value(dict): 생성되거나 접근되는 데이터입니다. 이 dict의 내용은 접근되는 resource와 action에 따라 다릅니다. 더 세밀한 접근 제어를 얻는 방법에 대한 정보는 아래의 범위가 지정된 authorization handler 추가를 참조하세요.
- 사용자의 ID를 리소스의 메타데이터에 추가합니다.
- 사용자가 자신이 소유한 리소스만 볼 수 있도록 메타데이터 필터를 반환합니다.
2. 비공개 대화 테스트
authorization을 테스트하세요. 올바르게 설정했다면 모든 ✅ 메시지가 표시됩니다. 개발 서버가 실행 중인지 확인하세요(langgraph dev 실행):
- 각 사용자는 자신의 thread를 생성하고 채팅할 수 있습니다
- 사용자는 서로의 thread를 볼 수 없습니다
- thread 목록은 자신의 것만 표시합니다
3. 범위가 지정된 authorization handler 추가
광범위한@auth.on handler는 모든 authorization 이벤트와 일치합니다. 이것은 간결하지만 value dict의 내용이 잘 범위가 지정되지 않고 모든 리소스에 동일한 사용자 수준 접근 제어가 적용된다는 것을 의미합니다. 더 세밀하게 제어하려면 리소스에 대한 특정 action을 제어할 수도 있습니다.
src/security/auth.py를 업데이트하여 특정 리소스 유형에 대한 handler를 추가하세요:
- thread 생성
- thread 읽기
- assistant 접근
@auth.on.assistants)는 assistants 리소스에 대한 모든 action과 일치합니다. 각 요청에 대해 LangGraph는 접근 중인 리소스와 action과 일치하는 가장 구체적인 handler를 실행합니다. 이는 광범위하게 범위가 지정된 “@auth.on” handler가 아닌 위의 네 가지 handler가 실행된다는 것을 의미합니다.
테스트 파일에 다음 테스트 코드를 추가해 보세요:
다음 단계
이제 리소스에 대한 접근을 제어할 수 있으므로 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다:- 인증 제공자 연결로 이동하여 실제 사용자 계정을 추가합니다.
- authorization 패턴에 대해 자세히 알아봅니다.
- 이 튜토리얼에서 사용된 인터페이스와 메서드에 대한 자세한 내용은 API 참조를 확인하세요.
Connect these docs programmatically to Claude, VSCode, and more via MCP for real-time answers.

